Chain in Surveying | Types of Chain Surveying | Equipment used in Chain Surveying | Working Procedure in Chain Surveying
What is chain surveying
Chain Surveying – Chain surveying is used for measuring only horizontal linear measurement.
Chain surveying is suitable for open ground and small extent area. Chain in surveying only simple details are know. The principle of chain surveying / chain triangulation is to provide a skeleton or framework consisting of a number of connected triangles. For better results, the framework should consist of triangles which are as nearly equilateral as possible.
Equipment used in Chain Surveying
- Chains
- Arrows
- Peg
- Ranging rod
- Plumb bob
- Hammer
Chains
Types of Chain used in Surveying
i. Metric chain
iii. Engineers chain
iv. Revenue chain
Metric Chain
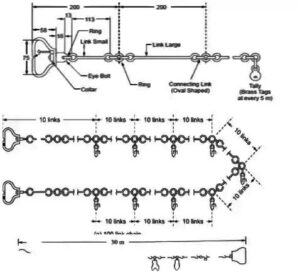
Metric Chain – Metric chains are generally of 5 m, 10 m, 20 m, & 30 m, length. Details about the metric chain IS: 1492-1970 covers the requirements of the metric chain.
In 5 m, 10 m, chain tallies are provided at every one meter length to make reading easier while these tallies are provided at every 5 m length in 20 m and 30 m chains. In 20 and 30 chains, Small brass rings are provided at every one meter length except where tallies are provided.
Gunter’s Chain
Gunter’s Chain – A gunter’s Chain is 66 feet long consist of 100 links, each link 0.66 feet long (7.92 inches). It was originally adopted for convenience in land measurement since 10 square chains are equal to 1 acre, also while measuring linear measurement.
Engineers Chain
Engineers Chain – Being 100 feet long and consisting of 100 links, each link being 1 feet. At every 10 links brass tags are fastened with notches indicating 10 links segments. The uses of engineers’ chains are generally measured to Feet.
Revenue Chain
Revenue Chain – The Revenue chain is 33 feet long and consists of 10 links each link being 2 1/16 feet long, the chain in surveying used for measuring field’s in cadastral survey.
 |
| Revenue chain |
NOTE – Chain may get altered (it’s length) due to continuous using either it’s length is being shortened due to bending of links or it’s length gets elongated due to starching of links or opening of the connecting rings. Thus don’t give accurate measurement.
So; it chain must be tested time to time either with the reference to a tape or by measuring with a permanent test gauge.
Arrows
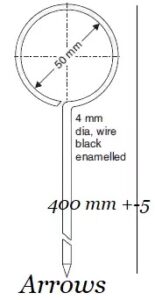
Arrows – These are the marking pens made of steel wire and generally 10 arrows are provided with a chain survey. Length may vary from 25 mm to 50 mm but specified length as per IS-Code. The arrow is made sharp and the other end is bent into a loop or circle for ease of carrying. The use of arrows is inserted into the ground after every chain length measured on the ground.
 |
| Arrow |
Pegs
Pegs – Pegs are used to mark the position station or terminal point of a survey line. They are driven in the ground with the help of the wooden hammer and kept 4 cm above the ground surface. The dimensions of pegs are generally 15 cm long and 3 cm squared in the top. Pegs are usually available of wooden.
 |
| Pegs |
Ranging Rod
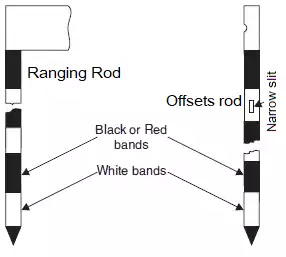
Ranging Rod – Ranging rods are 2 m – 3 m high rods of steel or well seasoned wood using the ranging of point. They are painted in alternate colours of the band either white & black, white & red or black, white and red in succession. the band is of length 20 cm, so that can be used for the rough measurement of smaller length 2 m ranging rod being more common. They are circular or octagonal in a cross-section of three cm diameter and are almost invisible at a distance of 200m.
They are provided with a yellow or white flag 0f 30 – 50 sq. cm area tied near it’s stop.
 |
| Ranging rod |
Ranging poles – They are similar to ranging rod except they are very high in length (4 m–8 m) they are similar to ranging rod and are used in very long survey lines or for hilly reasons. The foot of each pole is sunk about 0.5 meter into the ground.
Plumb bob
Plumb bob – These are used for centering i.e; to transfer the point exactly to the ground station. while instrument compass level, plane table, theodolite, chain in surveying etc,
While chaining along sloping ground, it is used to transfer the point exactly on the ground.
 |
| Plumb bob |
Hammer
Hammer – General used.
Ranging in Surveying
When length of line to be surveyed is within chain length and tape length, Then there is no difficulty but when the length is greater than the chain length, when the intermediate points should be fixed in a well straight manner by ranging.
Type of Ranging
1. Direct Ranging
2. Indirect Ranging
1. Direct Ranging
1. Ranging by eye.
2. Ranging by line ranger.
Ranging by eye – Let A and B are the two end points of a surveying and P is the intermediate point established on the ground. Surveyor stands for station A and the one ranging rod is erected at point B. Then assistance goes with another ranging rod that approximately stands for the line AB and the surveyor instructs the assistance to move transverse to the chain line, till he is line in the AB. similarly more than intermediate points are established by the above procedure.
Ranging by line ranger – A line ranger either consists of two plane mirrors or two right angled isosceles prisms. Placed one above other where diagonals are silvered so as two reflect incidental rays.
In such a case, ranging is done indirectly by selecting two intermediate points P & Q very near to the proposed survey line. Such that from P, both Q & B are visible and from Q both P & A are visible.
The range a point ‘P’ two ranging rods at the ends A & B and the surveyor at P hold the line ranger very near to line AB.
The lower prism ABC receives the ray from, A which are reflected back towards the observer similarly, the upper prism DCB receives the ray from B which are reflected back by its diagonals towards observer thus, the observer views the images of ranging rods A & B which may not be in same vertical line.
The surveyor moves with the line ranger. The point where two images coincide in the line ranger is the point in the line with two fixed ranging rods.
2. Indirect Ranging
Indirect Ranging – This ranging is done when the two points to be surveyed are not intervisible to each other due to high levelled ground in between or due to very long distance.
 |
| Indirect ranging |
In such a case, ranging is done indirectly by selecting two intermediate points M & N very near to the proposed survey line. Such that from M, both N & B are visible and from N both M & A are visible.
Code signals of ranging
|
|
|||||
|
Signal by the Surveyor |
Action by the Assistant |
|||
|
1. Rapid sweep with right hand |
Move considerably to the right |
|||
|
2. Slow sweep with right hand |
Move slowly to the right |
|||
|
3. Right arm extended |
Continue to move to the right |
|||
|
4. Right arm up and moved is the right |
Plumb the bob is right |
|||
|
5. Rapid sweep with left hand |
Move considerably to the left |
|||
|
6. Slow sweep with left hand |
Move slowly to the left |
|||
|
7. Left arm extended |
Continue to move to the left |
|||
|
|
|
|
||
|
8. Left arm up and moved is the left |
Plumb the bob is left |
|||
|
9. Both hand above head and then brought down |
Correct |
|||
|
10. Both hand extended forward horizontally and the hands depressed briskly |
Fix the rod |
|||
Station and line used in chain surveying
Station used in Chain Surveying
- Main Station
- Subsidiary Station (Tie Station)
Main Station
Main Station – Main stations are the end of the lines, which command the boundaries of the survey, and the lines joining the main station are called main surveying lines or the chain surveying lines.
Subsidiary Station
Subsidiary Station – Subsidiary or tie stations are the points selected on the main survey lines, where it is necessary to locate the interior details such as fences, hedges, buildings etc.
Line used in Chain Surveying
- Base line
- Check line
- Tie line
Base line
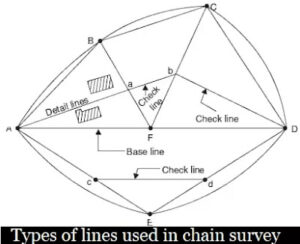
Base line – It is the main and longest line, which passes approximately through the centre of the field. All the other measurements to show the details of the works are taken with respect to this line.
Check line
Check line – A check line also termed as a proof line is a line joining the apex of a triangle to some fixed point on any two sides of a triangle. It is measured to check the accuracy of the framework. The length of the check line measure in the field must agree with its length on the plan.
Tie line
Tie line – A tie line joins the two fixed points on the main surveyed line. It helps to check the accuracy of surveying and to locate the interior details of nearby objects. In the framework more tie lines are provided depending upon the circumstances.
 |
| Line used in surveying |
Factor affecting survey station selection in surveying
- It is clearly visible.
- The lines are level ground as far as possible.
- Main lines are triangles.
- Each triangle must be provided with a check line.
- Avoid the obstacles through the main survey line.
- Getting short offset.
Offsets of chain in surveying
Offsets are the lateral measurement from the surveying lines to fixed the position of different objects with respect to the survey lines.
Types of Offsets
- Perpendicular Offsets
- Oblique Offsets
Perpendicular Offsets
Perpendicular Offsets – When the angle of offsets is 90 degrees . It is called perpendicular offsets.
- 3 – 4 – 5 method (Pythagoras theorem)
- Swing method
3 – 4 – 5 method – 3 – 4 – 5 method is used to draw perpendicular offsets & is based on the principle of pythagoras theorem.
Swing method – Swing method is also used to draw perpendicular offsets in chains in surveying and other surveys. It is based on the principle that the shortest distance between any two points is nothing but the perpendicular distance.
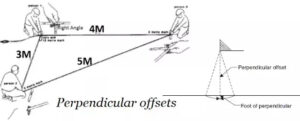 |
| Perpendicular offsets |
Oblique Offsets
Instrument used for drawing offsets
- Cross Staff
- Optical Square
- Prism Square
- Site Square
Cross Staff
Cross Staff – Cross staff are also available for three types
- Open Cross Staff
- French Cross Staff
- Adjustable Cross Staff
Open Cross Staff – Since the open cross staff is light and strong so it is more commonly used to draw the offsets at right angle.
French Cross Staff – French cross staff is used for setting an offset at the angle of 45 degree.
Adjustable Cross Staff – Adjustable Cross Staff is used for setting an offset at any angle.
Optical Square
Optical Square – It is more accurate then the cross staff and is used for setting out accurately the long offsets. It is a smaller compact hand instrument based on the principle of reflection.
The principle underlying the construction of reflecting instrument may be started as if these are two plane mirror whose reflecting surfaces makes a given angle with each other and if the ray of light is reflected successively from both of them then the angle between the first incident ray and last reflected ray is twice the angle between the two mirror.
In case of a optical square the angle between the first incident ray and the last reflected ray is 90°.
Prism Square
Prism Square – Prism square is a modern and precise instrument and used similarly to the optical square.
Site Square
Site Square – It is used in conjunction with a datum rod screwed into the base of the instrument. It is connected with two telescopes.
Working in Chain Surveying in offsets
A ray from ranging rod at Q passes through lower unsilvered portion of mirror at B. and is seen directly by eye at silt E. Another ray from the object at P is received by the mirror at A and is reflected towards the mirror at B which reflected towards the eye thus, the images of P & Q are visible at B.
Procedure in Chain Surveying
Reconnaissance in chain surveying
- Reconnaissance – The preliminary inspection of the to be surveyed is called reconnaissance. The surveyor inspect the area to be surveyed, survey or prepare index sketch or key plan. He should also investigate the difficulties of plotting the survey line and other work.
Marking Station in Chain Surveying
- Marking Station – Survey fixed up the require no of stations at the place from where the maximum possible station can be plotted.
Some Operation :-
- Fixing of ranging rod and poles.
- Driving Pegs.
- Making a cross (╳) if ground is hard.
- Digging & fixing a stone.
- Then selected the way for passing the main line. Which should be horizontal and clean as possible and should pass approximately through the centre of work.
- The ranging rods are fixed on the station.
- After fixing the stations, chain in could be started.
- Make ranging wherever necessary.
- Measure the chain edge and offsets.
- Enter the observation and measurement in the field book.
Obstacles in chain surveying
- Obstacles to ranging.
- Obstacles to chaining.
- Obstacles to both ranging and chaining
Field book mention chain in surveying
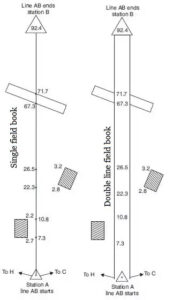
A field book is a standard oblong for pocket book where all the observation and measurement taken during chain surveying is to be recorded.
It is 200 m long and 120 mm wide. It is open length wise . It is a two types.
2. Double line field book.


Pingback: Contour | Method Of Contour Surveying | Contour Interval | Gradient | Direct Method | Indirect Method | Contour Map & Uses – civilnotebook.com
Pingback: Chlorination | Type of chlorination | Residual Chlorine - civilnotebook.com
Pingback: Piles | Types of Pile | Concrete Piles | Timber Piles | Steel Piles | Composite Piles