Consistency of Soil | Stage | Consistency Limit | Liquid – Plastic – Solid |
Consistency of Soil.
- Consistency
of soil means ease with which a soil paste can be deformed. - It is
denoted the degree of firmness of soil which may be referred as soft, stiff
or hard soil depending upon its water content. - This behavior
of phase change with the amount of water is known as consistency.
Stage of Consistency.
There are
three stage of consistency liquid, plastic and solid. Increase the water content
in soil. Soil passes from solid to plastic & plastic to liquid stage. Similarly If we heat a liquid paste of soil to reduce its water and decrease in
volume. It’s called shrinkage of soil.
Shrinkage
of soil up to a certain point after that soil volume mass will be remains
constant. These are the different stage of consistency. [ what is brick ]
Consistency Limit.
Consistency
of soil is a relative to its water content and water content at which soil
changes from one stage of consistency to the another stage of consistency is
called as consistency limit or Atterberg limit of consistency.
- Depending
upon the water content soil may be a stiff stage, plastic stage or liquid
stage. In 1911 Atterberg define the boundary line water content at which soil change from one stage to another stage. - Casagrande represent in 1932 improved testing procedure along Atterberg testing procedure.
Atterberg Analysis of Soil :-
- Liquid
stage of consistency. - Plastic stage of consistency.
- Semisolid stage of
consistency. - Solid stage of consistency
Liquid Limit (WL) :-
defined as the minimum water content at which the plastics soil changes into
liquid soil and liquid stage of consistency behave like liquid. [ W.S.M & L.S.M ]
It can also
be defined as the water content at which soil passes from liquid stage of
consistency to plastic stage of consistency and vice-versa.
Liquid
stage of consistency determined by any standard experimental method.
All the
soil at liquid limit are found to have negligible shear strengths of 2.7 KN/m3. Which
can be just measure.
Determination of Liquid Limit. ( IS – 2720, Part 5-1985 )
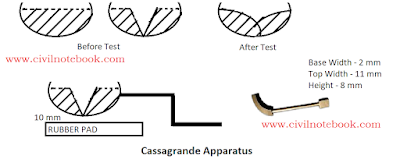
- This test is
performed in a laboratory; Standard apparatus is used known as casagrande’s
apparatus. - In casagrande
apparatus brass Cup mounted on a hard rubber pad. This brass Cup can be raised
and made to fall on the hard rubber pad. - By the
screws distance of the fall can be regulated.
- This test
is performed for the soil particle passing through 425µ (micron). - From the
point of view of a determination of liquid limit, which may also be defined as
the minimum water content at which a part of soil cut by a Standard tool
flow together by a distance of 1/2 inch in exactly 25 number of blows. [chain surveying] - In order to
find the liquid limit, this test is performed at different water content and
gross cross ponding number of blows required to flow the soil together by a
distance of 1/2 inch is noted and the result is expressed in the form of curve, called as flow curve.
Plastic Limit (WP) :-
Plastic
limit is defined as the minimum water content at which soil remains plastic
stage of consistency.
It may also
be defined as the water content at which soil passes from plastic stage of
consistency to semi-solid stage of consistency and vice-versa.
Determination of Liquid Limit. ( IS – 2720 )
- About 15 gm of air dried soil and passing through 425µ (micron) sieve is taken for plastic
limit determination. [ concrete compaction ] - Make paste of soil passing through 425µ (micron) sieve and
lift it for some times. - Take about 8 gm of soil and the rolled it with
finger on a glass plate. - Rate of
Rolling should be about 80 to 90 times per minute to from thread of 3 mm diameter.
- Plastic
limit is defined as the minimum water content at which soil begin to crumble
when rod into a thread of 3 mm diameter.
|
Type of Soil |
Wp (%) |
|
Gravel Sand |
Non Plastic |
|
Silt |
20 – 25 % |
|
Clay ( Alluvial ) |
25 – 50 % |
|
Clay ( Block Cotton ) |
200 – 250 % |
|
Clay ( Bentonite ) |
200 – 400 % |
Shrinkage Limit (WP) :-
It is define as the maximum water content below which any reduction in the water content on the soil has no effect over the volume of soil as below shrinkage limit water is being replaced by air of equal volume.
It may also be define as the minimum water content at which soil is completely saturated.
It may also be define as the water content at which soil passage from solid stage of consistency to semi-solid stage of consistency or vice-versa.
Determination of Shrinkage Limit. ( IS – 2720, Part 6-1972 )
- Passing 425 micron sieve is taken 30 gm of soil sample in an
evaporating dish. - The soil sample is mixed with sufficient quantity of water
to bring the soil to a consistency that it may flow. [ type of brick bond ] - Mixed soil sample is placed in shrinkage dish in 3 equal quantities
and fill the dish and excess soil sample is removed and weighed the dish with
the soil. - Allowed to dry till the colour changes from dark to light.
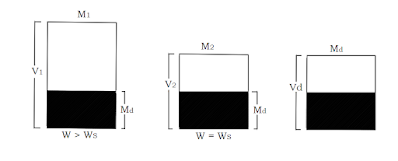
- Consider a sample of soil having W greater than shrinkage
limit and having mass and volume M1 and V1. - The sample is subjected to drying in oven at 110℃ and at particular stage of drying where the W
is equal to shrinkage limit it’s mass and volume is M2 and V2 and at completely
drying let it’s mass and volume be Md and Vd.
1. What is consistency of soil.
Consistency of soil means ease with which a soil paste can be deformed.
2. Shrinkage of soil.
There are three stage of consistency liquid, plastic and solid. Increase the water content in soil. Soil passes from solid to plastic & plastic to liquid stage. Similarly If we heat a liquid paste of soil to reduce its water and decrease in volume. It’s called shrinkage of soil.
3. Atterberg analysis of soil.
Liquid stage of consistency.
Plastic stage of consistency.
Semisolid stage of consistency.
Solid stage of consistency.
4. What is plastic limit
Plastic limit is defined as the minimum water content at which soil remains plastic stage of consistency.
5. Define liquid limit.
Liquid limit is defined as the minimum water content at which the plastics soil changes into liquid soil and liquid stage of consistency behave like liquid.







Pingback: Piles | Types of Piles | Concrete Piles | Steel Piles | Timber Piles | Composite Piles | Advantages & Disadvantages Of Piles - civilnotebook.com
Pingback: Spread Footing | 6 types | Advantages and disadvantages
Pingback: What is Concrete Compaction | Method | Types | Hand Compaction | Mechanical Compaction | Pressure and Jolting Compaction | - civilnotebook.com