Sedimentation | Principle of sedimentation tank | Design parameter of sedimentation tank | Type of sedimentation tank
Sedimentation
Sedimentation in a natural process to remove the suspended particles such as sand, silt, clay etc.
All the particles, whose specific gravity is more than one, try to settle down by ground surface but resist the turbulence and flow velocity. In a sedimentation tank easily reducing the turbulence and flow velocity and particles settle down. Then settle particles are removed.
Principle of sedimentation tank
- In the sedimentation tank, only suspended impurities are removed. Whose specific gravity more than water specific gravity (1) .
- Due to turbulence in water impurities will settle down. so in figure.
- Thus, reducing the velocity of water to cause the settling down of suspended particles by natural process (gravity) is the principle of a sedimentation tank.
Design parameter of sedimentation tank
- Detention time
- Surface loading rate
- Flow velocity
Detention time
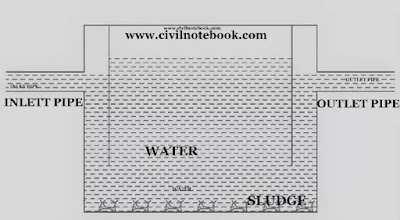
Detention time – Detention time is the time taken by water to travel from inlet pipe of sedimentation tank to outlet pipe of sedimentation tank is called detention time in sedimentation tank. [ Size of brick ]
Generally the detention time of a sedimentation tank is 4 – 8 hours. Detention time of sedimentation tank is calculated by following formula –
Detention time = Volume of tank / Discharge
Dt = V/Q
Surface loading rate
Surface loading rate – Surface loading rate is defined as the rate of settlement of suspended particles in a given surface area of a sedimentation tank.
Generally the surface loading rate of a sedimentation tank lies between 500 to 700 lit/hr/m2. Surface loading rate of sedimentation tank is calculated by following formula –
Surface loading rate = Discharge / Surface area
Vo = Q / B x L
Unit of Vo = m3 / day / m2
Lit / hr / m2
Flow velocity
Flow velocity – It is a velocity in which water enters into the sedimentation tank.
Generally flow velocity of a sedimentation tank lies between 0.15 – 0.9 m/min. It is calculated by the following formula –
Flow velocity = Discharge / Surface area
VH = Q / B x H
Note – Particles completely get removed when the particle has settled velocity more than or equal to surface overflow rate.
Type of sedimentation tank
- Sedimentation tank Classified on the basis of flow direction
- Sedimentation tank Classified on the basis of Shape
- Sedimentation tank Classified on the basis of process
- Sedimentation tank Classified on the basis of location
| Classification on the basis of | Types | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Flow direction | Horizontal flow sedimentation tank | Vertical flow sedimentation tank | |
| Shape | Rectangular sedimentation tank | Circular sedimentation tank | Hopper bottom sedimentation tank |
| Process | Feel & draw sedimentation tank | Continuous sedimentation tank | |
| Location | Primary sedimentation tank | Secondary sedimentation tank |
Sedimentation tank Classified on the basis of flow direction
- Horizontal flow sedimentation tank
- Vertical flow sedimentation tank
Horizontal flow sedimentation tank
Horizontal flow sedimentation tank – Horizontal flow sedimentation tanks are generally preferred for rectangular shape sedimentation tanks because they need to flow more length to settle down the suspended particles. The maximum permissible velocity of water in horizontal flow sedimentation tank is 0.3m / sec.
Vertical flow sedimentation tank
Vertical flow sedimentation tank – Vertical flow sedimentation tank are generally circular in shape and water flow takes in a vertical direction. In the vertical sedimentation tank, Hopper bottom sedimentation tank are provided at the bottom to collect the sludge and suspended particle.
Sedimentation tank Classified on the basis of Shape
- Rectangular sedimentation tank
- Circular sedimentation tank
- Hopper bottom sedimentation tank
Rectangular sedimentation tank
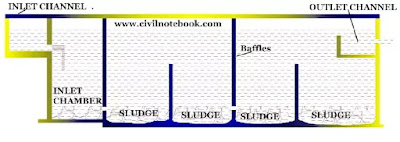
Rectangular sedimentation tank – Rectangular tanks are widely used and mostly preferred sedimentation tank. In this type of sedimentation tank flow is placed in horizontal direction and baffle walls are provided to prevent short circuiting. Rectangular sedimentation tank are suitable for large capacities of water treatment plants and maintenance costs are low compared to vertical sedimentation tank.
Circular sedimentation tank
Circular sedimentation tank – Vertical flow type sedimentation tank are preferred for circular sedimentation tank.
In circular sedimentation tank sludge is collected mechanically and collected sludge carried through sludge pipe at the bottom, Circular sedimentation tank are highly efficient for clarification but they are costly and uneconomically compared to rectangular sedimentation tank. [ Class of brick | Properties of brick]
 |
| Circular Sedimentation Tank |
Hopper bottom sedimentation tank
Hopper bottom sedimentation tank – In this type of sedimentation tank, The bottom of the sedimentation tank is hopper shaped and the upper face of the sedimentation tank is the same as a rectangular sedimentation tank. And sludge is collected at the bottom.
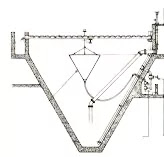 |
| Hopper Bottom Sedimentation Tank |
Sedimentation tank Classified on the basis of process
- Feel & draw sedimentation tank
- Continuous sedimentation tank
Feel & draw sedimentation tank
Feel & draw sedimentation tank – In this type of sedimentation tank water is stored for some time in the sedimentation tank. The time it takes for water to be stored in a sedimentation tank is 24 hours. In 24 hours the suspended particles settle down at the bottom of the sedimentation tank. After 24 hours The suspended particles are settled down, then the raw water is discharged from the outlet pipe in the further process of the treatment plant. and then all the suspended particles which settle down the bottom of the sedimentation tank are removed.
This removal action of suspended particles in the sedimentation tank are required for the 6 – 12 hours, so one complete action of feel & draw type sedimentation tank are required for 30 – 40 hours. [ Chain Surveying – Type of chain – Equipment used in chain surveying ]
Continuous sedimentation tank
Continuous sedimentation tank – In this type of sedimentation tank, water is not allowed to rest in the sedimentation tank. Water continuously flows from inlet pipe to outlet pipe but flow velocity of water or discharge is very slow compared to fill & draw type sedimentation tanks. In continuous type of sedimentation tanks generally rectangular or circular shape tanks are used. Hopper bottom sedimentation tanks are not used.
In this type of tank the flow may be either in horizontal direction or in vertical direction.
Sedimentation tanks are classified on the basis of location
Sedimentation tanks are classified on the basis of location – On the basis of location sedimentation tank, tank are classified into two types
- Primary sedimentation tank
- Secondary sedimentation tank
Primary sedimentation tank
Secondary sedimentation tank
Secondary sedimentation tank – Secondary sedimentation tank is the same as the primary sedimentation tank. All the working processes are the same as a primary sedimentation tank but suspended particles, sludge or oily matter are removed for the Anaerobic process.
Plain sedimentation
Plain sedimentation – Sedimentation and coagulation processes are done simultaneously is called plain sedimentation. It means, Sedimentation are removed the suspended particles and coagulation removes the colloidal particles.
In plain sedimentation, very fine suspended particles are not removed because silt particles 0.06 mm size require 10 hrs for settling down in 3 m sedimentation tank and 0.002 mm size of suspended particles are required for 4 days for settling down in sedimentation tank. In colloidal particles water contains electrically charged so colloidal particles continuously in motion and due to gravitational force particles never settle down in the sedimentation tank. So it is necessary to remove the fine clay and colloidal particles. Sedimentation with coagulation is the process to easily remove colloidal particles from water.
Advantage of plain sedimentation
- Reduce the cost of cleaning chemicals in the coagulation basin.
- In this treatment process low chemical quantities are required.
- No chemical loss in the plain settling basin for sludge discharged.
- It lightens the load on further processes of the water treatment plant.
- Further purification processes can be controlled easily, because plain sedimentation delivers less variable quality of water.
- [ What is concrete compaction – Method of concrete compaction – Hand compaction – Mechanical compaction]
FAQ’s
Question 01. What is sedimentation?
Answer – Sedimentation is the process to remove the suspended particles in the raw water in a water treatment plant.
Question 02. Type of sedimentation tank
Answer – 01. Rectangular sedimentation tank 02. Circular sedimentation tank 03. Hopper bottom sedimentation tank 04. Feel and draw sedimentation tank 05. Continuous sedimentation tank 06. Primary sedimentation tank 07. Secondary sedimentation tank.
Question 03. How do you calculate detention time in a sedimentation tank
Answer – Detention time of sedimentation tank is calculated by following formula –
Detention time = Volume of tank / Discharge
Dt = V/Q
Question 04. The detention period for plain sedimentation water tank is usually
Answer – Generally the detention time of a sedimentation tank is 4 – 8 hours.

Pingback: Chlorination | Type of chlorination | Residual Chlorine - civilnotebook.com
Pingback: Screening in water treatment plant | Type of screening in water treatment plant - civilnotebook.com
Pingback: Piles | Types of Piles | Concrete Piles | Steel Piles | Timber Piles | Composite Piles | Advantages & Disadvantages Of Piles - civilnotebook.com